Customers usually turn to the internet to get information and buy products and services. Towards that end, most organizations have websites.Most websites store valuable information such as credit card numbers, email address and passwords, etc. This has made them targets to attackers. Defaced websites can also be used to communicate religious or political ideologies etc.
In this tutorial, we will introduce you toweb servers hacking techniques and how you can protect servers from such attacks.
Web server vulnerabilities
A web server is a program that stores files (usually web pages) and makes them accessible via the network or the internet. A web server requires both hardware and software. Attackers usually target the exploits in the software to gain authorized entry to the server. Let’s look at some of the common vulnerabilities that attackers take advantage of.
- Default settings– These settings such as default user id and passwords can be easily guessed by the attackers. Default settings might also allow performing certain tasks such as running commands on the server which can be exploited.
- Misconfigurationof operating systems and networks – certain configuration such as allowing users to execute commands on the server can be dangerous if the user does not have a good password.
- Bugs in the operating system and web servers– discovered bugs in the operating system or web server software can also be exploited to gain unauthorized access to the system.
In additional to the above-mentioned web server vulnerabilities, the following can also led to unauthorized access
- Lack of security policy and procedures– lack of a security policy and procedures such as updating antivirus software, patching the operating system and web server software can create security loop holes for attackers.
Types of Web Servers
The following is a list of the common web servers
- Apache– This is the commonly used web server on the internet. It is cross platform but is it’s usually installed on Linux. Most PHP websites are hosted on Apache servers.
- Internet Information Services (IIS)– It is developed by Microsoft. It runs on Windows and is the second most used web server on the internet. Most asp and aspx websites are hosted on IIS servers.
- Apache Tomcat – Most Java server pages (JSP) websites are hosted on this type of web server.
- Other web servers – These include Novell’s Web Server and IBM’s Lotus Domino servers.
Types of Attacks against Web Servers
Directory traversal attacks– This type of attacks exploits bugs in the web server to gain unauthorized access to files and folders that are not in the public domain. Once the attacker has gained access, they can download sensitive information, execute commands on the server or install malicious software.
- Denial of Service Attacks– With this type of attack, the web server may crash or become unavailable to the legitimate users.
- Domain Name System Hijacking – With this type of attacker, the DNS setting are changed to point to the attacker’s web server. All traffic that was supposed to be sent to the web server is redirected to the wrong one.
- Sniffing– Unencrypted data sent over the network may be intercepted and used to gain unauthorized access to the web server.
- Phishing– With this type of attack, the attack impersonates the websites and directs traffic to the fake website. Unsuspecting users may be tricked into submitting sensitive data such as login details, credit card numbers, etc.
- Pharming– With this type of attack, the attacker compromises the Domain Name System (DNS) servers or on the user computer so that traffic is directed to a malicious site.
- Defacement– With this type of attack, the attacker replaces the organization’s website with a different page that contains the hacker’s name, images and may include background music and messages.
Effects of successful attacks
- An organization’s reputation can be ruined if the attacker edits the website content and includes malicious information or links to a porn website
- The web server can be used to install malicious software on users who visit the compromised website. The malicious software downloaded onto the visitor’s computer can be a virus, Trojan or Botnet Software, etc.
- Compromised user data may be used for fraudulent activities which may lead to business loss or lawsuits from the users who entrusted their details with the organization
Web server attack tools
Some of the common web server attack tools include;
- Metasploit– this is an open source tool for developing, testing and using exploit code. It can be used to discover vulnerabilities in web servers and write exploits that can be used to compromise the server.
- MPack– this is a web exploitation tool. It was written in PHP and is backed by MySQL as the database engine. Once a web server has been compromised using MPack, all traffic to it is redirected to malicious download websites.
- Zeus– this tool can be used to turn a compromised computer into a bot or zombie. A bot is a compromised computer which is used to perform internet-based attacks. A botnet is a collection of compromised computers. The botnet can then be used in a denial of service attack or sending spam mails.
- Neosplit – this tool can be used to install programs, delete programs, replicating it, etc.
How to avoid attacks on Web server
An organization can adopt the following policy to protect itself against web server attacks.
- Patch management– this involves installing patches to help secure the server. A patch is an update that fixes a bug in the software. The patches can be applied to the operating system and the web server system.
- Secure installation and configuration of the operating system
- Secure installation and configuration of the web server software
- Vulnerability scanning system– these include tools such as Snort, NMap, Scanner Access Now Easy (SANE)
- Firewalls can be used to stop simple DoS attacks by blocking all traffic coming the identify source IP addresses of the attacker.
- Antivirus software can be used to remove malicious software on the server
- Disabling Remote Administration
- Default accounts and unused accounts must be removed from the system
- Default ports & settings (like FTP at port 21) should be changed to custom port & settings (FTP port at 5069)
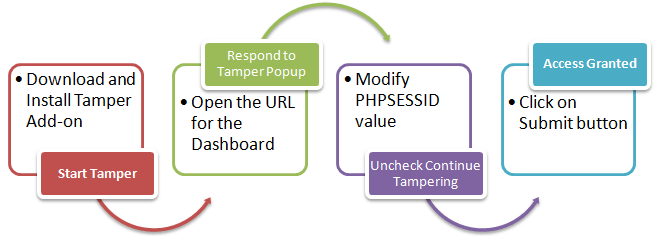
Hacking Activity: Hack a WebServer
In this practical scenario, we are going to look at the anatomy of a web server attack. We will assume we are targeting www.techpanda.org. We are not actually going to hack into it as this is illegal. We will only use the domain for educational purposes.
What we will need
Information gathering
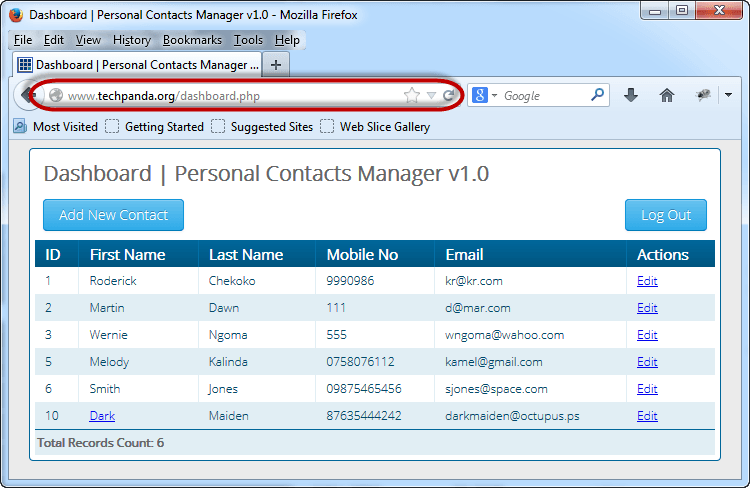
We will need to get the IP address of our target and find other websites that share the same IP address.
We will use an online tool to find the target’s IP address and other websites sharing the IP address
- Click on Check button
- You will get the following results

Based on the above results, the IP address of the target is 69.195.124.112
We also found out that there are 403 domains on the same web server.
Our next step is to scan the other websites for SQL injection vulnerabilities. Note: if we can find a SQL vulnerable on the target, then we would directly exploit it without considering other websites.
- Enter the URL www.bing.com into your web browser. This will only work with Bing so don’t use other search engines such as google or yahoo
- Enter the following search query
ip:69.195.124.112 .php?id=
HERE,
- “ip:69.195.124.112” limits the search to all the websites hosted on the web server with IP address 69.195.124.112
- “.php?id=” search for URL GET variables used a parameters for SQL statements.
You will get the following results
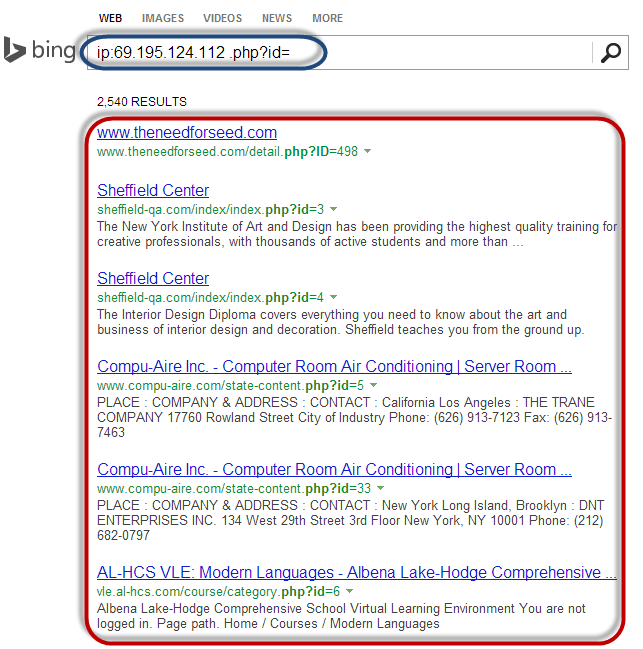
As you can see from the above results, all the websites using GET variables as parameters for SQL injection have been listed.
The next logic step would be to scan the listed websites for SQL Injection vulnerabilities. You can do this using manual SQL injection or use tools listed in this article on SQL Injection.
Uploading the PHP Shell
We will not scan any of the websites listed as this is illegal. Let’s assume that we have managed to login into one of them. You will have to upload the PHP shell that you downloaded from http://sourceforge.net/projects/icfdkshell/
- Open the URL where you uploaded the dk.php file.
- You will get the following window

- Clicking the Symlink URL will give you access to the files in the target domain.
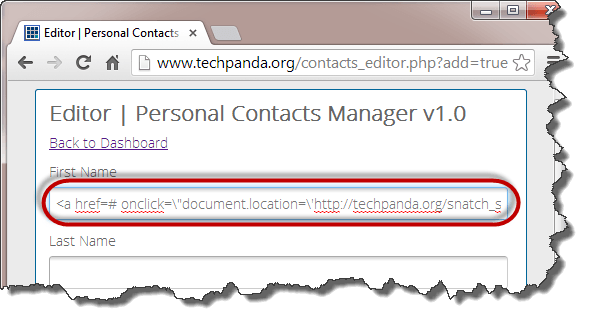
Once you have access to the files, you can get login credentials to the database and do whatever you want such as defacement, downloading data such as emails, etc.
Summary
- Web server stored valuable information and are accessible to the public domain. This makes them targets for attackers.
- The commonly used web servers include Apache and Internet Information Service IIS
- Attacks against web servers take advantage of the bugs and Misconfiguration in the operating system, web servers, and networks
- Popular web server hacking tools include Neosploit, MPack, and ZeuS.
- A good security policy can reduce the chances of been attacked