@ Malware
Software programs designed to damage or do unwanted actions on a computer. Common examples include: viruses, worms, trojan horses, spyware, and ransomware.
@ Phishing
Attacks sent via email and ask users to click on a link and enter their personal data. They include a link that directs the user to a dummy site that will steal a user’s information.
@ Password Attacks
Involves a third party trying to gain access to your systems by solving a user’s password.
@ Denial of Service Attacks (DoS or DDoS)
Attackers send high volumes of data or traffic through the network until the network becomes overloaded and can no longer function
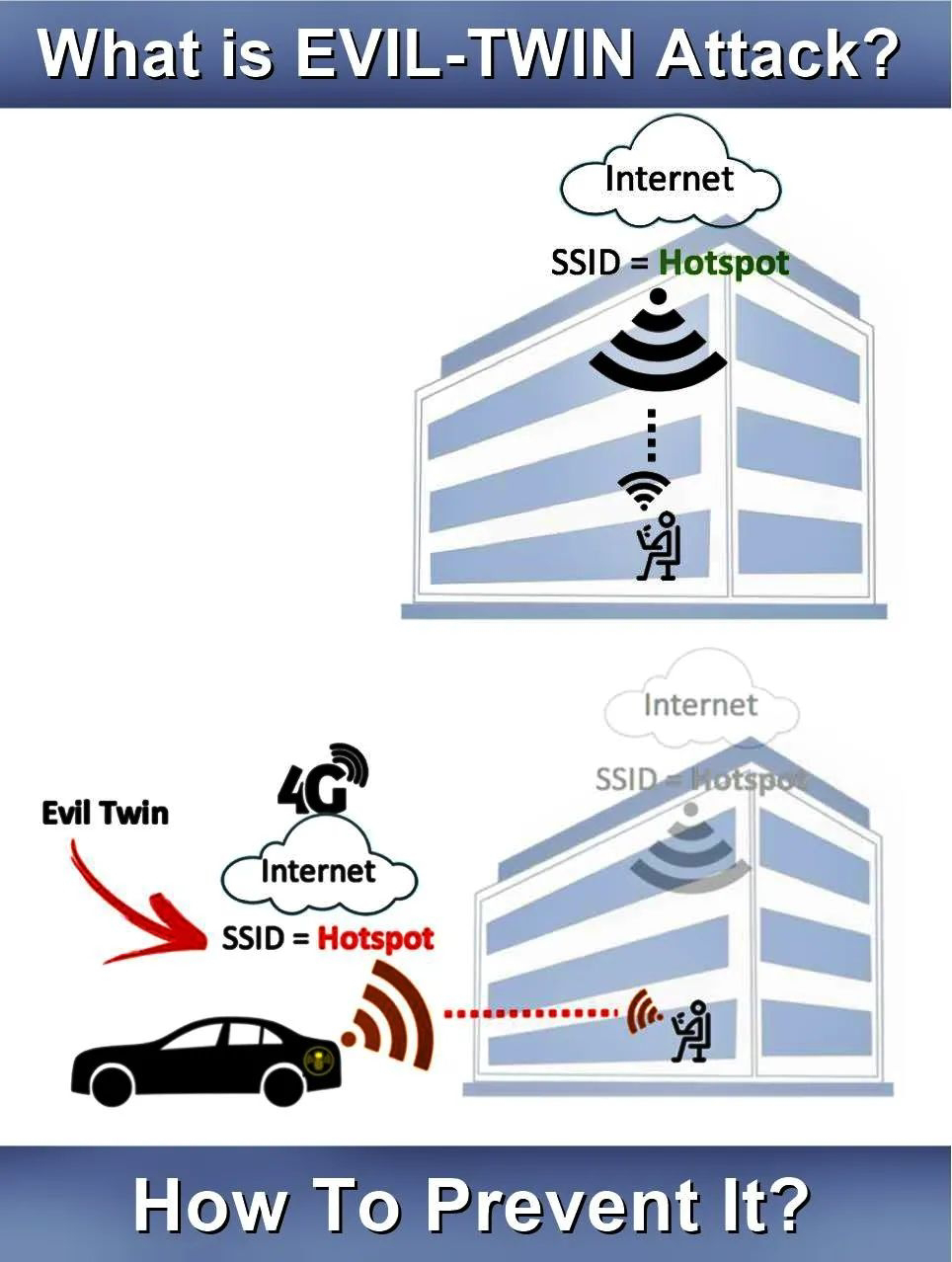
@ Man in the Middle (MITM)
Information is obtained from the end user and the entity the user is communicating with by impersonating the endpoints in an online information exchange (i.e. connection from smartphone to website).
@ Drive-by Downloads
A program is downloaded to a user’s system just by visiting the site. It doesn’t require any type of action by the user to download.
@ Malversating
Malversating ("malicious advertising") is the use of online advertising to spread malware. It typically involves injecting malicious or malware-laden advertisements into legitimate online advertising networks and webpages.
@ Rogue Software's
Rogue security software is a form of malicious software and internet fraud that misleads users into believing there is a virus on their computer and aims to convince them to pay for a fake malware removal tool that actually installs malware on their computer. It is a form of scareware that manipulates users through fear, and a form of ransomware
-


No comments:
Post a Comment