Information systems have made many businesses successful today. Some companies such as Google, Facebook, EBay, etc. would not exist without information technology. However, improper use of information technology can create problems for the organization and employees.
Criminals gaining access to credit card information can lead to financial loss to the owners of the cards or financial institute. Using organization information systems i.e. posting inappropriate content on Facebook or Twitter using a company account can lead to lawsuits and loss of business.
This tutorial will address such challenges that are posed by information systems and what can be done to minimize or eliminate the risks.
In this tutorial, you will learn –
- Cyber-crime
- Information system Security
- Information system Ethics
- Information Communication Technology (ICT) policy
Cyber-crime
Cyber-crime refers to the use of information technology to commit crimes. Cyber-crimes can range from simply annoying computer users to huge financial losses and even the loss of human life. The growth of smartphones and other high-end mobile devices that have access to the internet have also contributed to the growth of cyber-crime.
Types of cyber-crime
Identity theft
Identity theft occurs when a cyber-criminal impersonates someone else identity to practice malfunction. This is usually done by accessing personal details of someone else. The details used in such crimes include social security numbers, date of birth, credit and debit card numbers, passport numbers, etc.
Once the information has been acquired by the cyber-criminal, it can be used to make purchases online while impersonating himself to be someone else. One of the ways that cyber-criminals use to obtain such personal details is phishing. Phishing involves creating fake websites that look like legitimate business websites or emails.
For example, an email that appears to come from YAHOO may ask the user to confirm their personal details including contact numbers and email password. If the user falls for the trick and updates the details and provides the password, the attacker will have access to personal details and the email of the victim.
If the victim uses services such as PayPal, then the attacker can use the account to make purchases online or transfer funds.
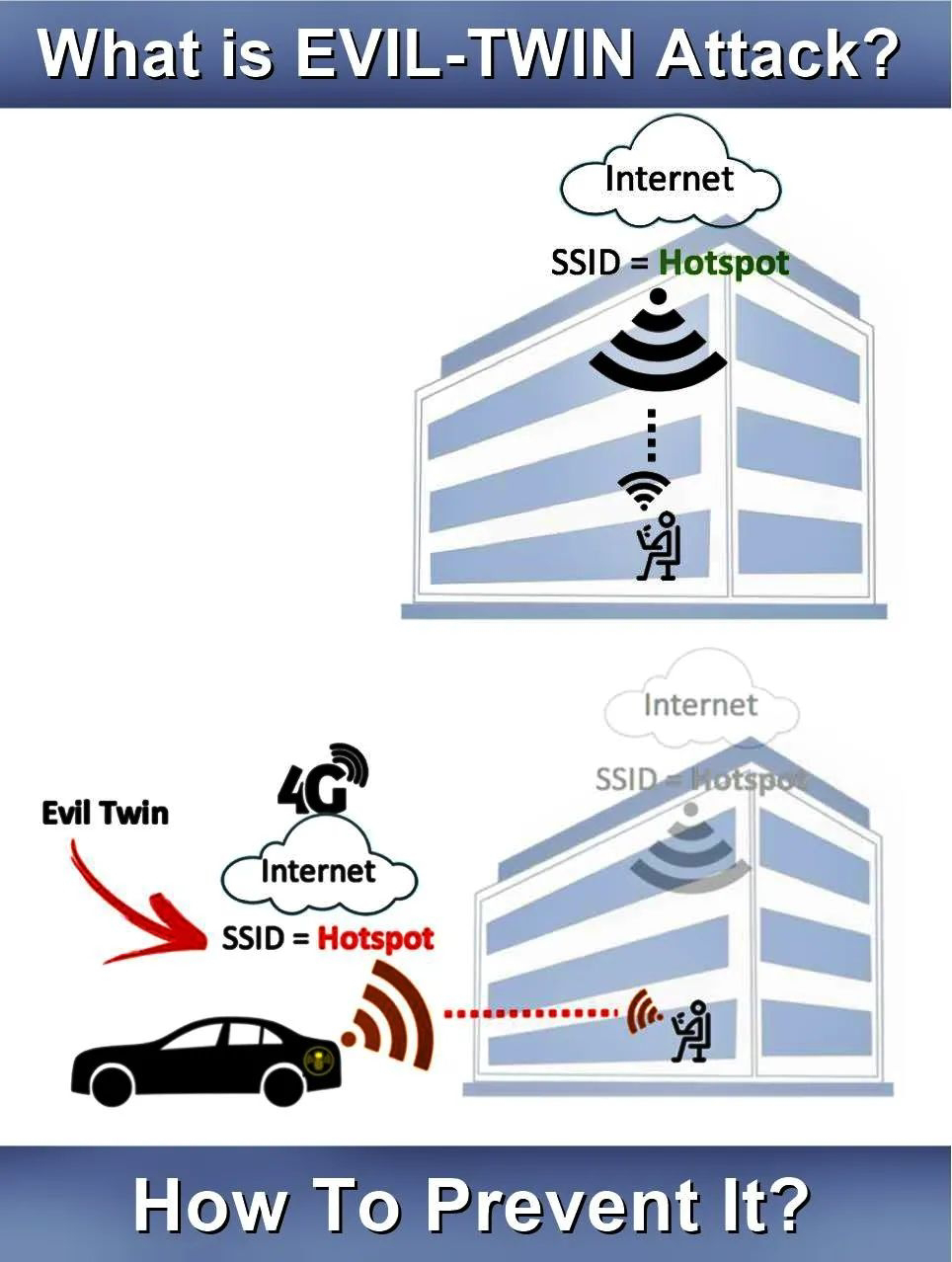
Other phishing techniques involve the use of fake Wi-Fi hotspots that look like legitimate ones. This is common in public places such as restaurants and airports. If an unsuspecting user logons into the network, then cyber-crimes may try to gain access to sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, credit card numbers, etc.
According to the US Department of Justice, a former state department employee used email phishing to gain access to email and social media accounts of hundreds of women and accessed explicit photos. He was able to use the photos to extort the women and threatened to make the photos public if they did not give in to his demands.
Copyright infringement
Piracy is one of the biggest problems with digital products. Websites such as the pirate bay are used to distribute copyrighted materials such as audio, video, software, etc. Copyright infringement refers to the unauthorized use of copyrighted materials.
Fast internet access and reducing costs of storage have also contributed to the growth of copyright infringement crimes.
Click fraud
Advertising companies such as Google AdSense offer pay per click advertising services. Click fraud occurs when a person clicks such a link with no intention of knowing more about the click but to make more money. This can also be accomplished by using automated software that makes the clicks.
Advance Fee Fraud
An email is sent to the target victim that promises them a lot of money in favor of helping them to claim their inheritance money.
In such cases, the criminal usually pretends to be a close relative of a very rich well-known person who died. He/she claims to have inherited the wealth of the late rich person and needs help to claim the inheritance. He/she will ask for financial assistance and promise to reward later. If the victim sends the money to the scammer, the scammer vanishes and the victim loses the money.
Hacking
Hacking is used to by-pass security controls to gain unauthorized access to a system. Once the attacker has gained access to the system, they can do whatever they want. Some of the common activities done when system is hacked are;
- Install programs that allow the attackers to spy on the user or control their system remotely
- Deface websites
- Steal sensitive information. This can be done using techniques such as SQL Injection, exploiting vulnerabilities in the database software to gain access, social engineering techniques that trick users into submitting ids and passwords, etc.
Computer virus
Viruses are unauthorized programs that can annoy users, steal sensitive data or be used to control equipment that is controlled by computers.
Information system Security
MIS security refers to measures put in place to protect information system resources from unauthorized access or being compromised. Security vulnerabilities are weaknesses in a computer system, software, or hardware that can be exploited by the attacker to gain unauthorized access or compromise a system.
People as part of the information system components can also be exploited using social engineering techniques. The goal of social engineering is to gain the trust of the users of the system.
Let's now look at some of the threats that information system face and what can be done to eliminate or minimize the damage if the threat were to materialize.
Computer viruses – these are malicious programs as described in the above section. The threats posed by viruses can be eliminated or the impact minimized by using Anti-Virus software and following laid down security best practices of an organization.
Unauthorized access – the standard convention is to use a combination of a username and a password. Hackers have learnt how to circumvent these controls if the user does not follow security best practices. Most organizations have added the use of mobile devices such as phones to provide an extra layer of security.
Let's take Gmail as an example, if Google is suspicious of the login on an account, they will ask the person about to login to confirm their identity using their android powered mobile devices or send an SMS with a PIN number which should supplement the username and password.
If the company does not have enough resources to implement extra security like Google, they can use other techniques. These techniques can include asking questions to users during signup such as what town they grew up in, the name of their first pet, etc. If the person provides accurate answers to these question, access is granted into the system.
Data loss – if the data center caught fire or was flooded, the hardware with the data can be damaged, and the data on it will be lost. As a standard security best practice, most organizations keep backups of the data at remote places. The backups are made periodically and are usually put in more than one remote area.
Biometric Identification – this is now becoming very common especially with mobile devices such as smartphones. The phone can record the user fingerprint and use it for authentication purposes. This makes it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access to the mobile device. Such technology can also be used to stop unauthorized people from getting access to your devices.
Information system Ethics
Ethics refers to rules of right and wrong that people use to make choices to guide their behaviors. Ethics in MIS seek to protect and safeguard individuals and society by using information systems responsibly. Most professions usually have defined a code of ethics or code of conduct guidelines that all professionals affiliated with the profession must adhere to.
In a nutshell, a code of ethics makes individuals acting on their free will responsible and accountable for their actions. An example of a Code of Ethics for MIS professionals can be found on the British Computer Society (BCS) website.
Information Communication Technology (ICT) policy
An ICT policy is a set of guidelines that defines how an organization should use information technology and information systems responsibly. ICT policies usually include guidelines on;
- Purchase and usage of hardware equipment and how to safely dispose them
- Use of licensed software only and ensuring that all software is up to date with latest patches for security reasons
- Rules on how to create passwords (complexity enforcement), changing passwords, etc.
- Acceptable use of information technology and information systems
- Training of all users involved in using ICT and MIS
Summary:
With great power comes great responsibility. Information systems bring new opportunities and advantages to how we do business but they also introduce issues that can negatively affect society (cybercrime). An organization needs to address these issues and come up with a framework (MIS security, ICT policy, etc.) that addresses them.

No comments:
Post a Comment